What is leaky gut syndrome?
A “leaky” gut is a permeable gut, meaning toxins are leaking out of the gut, or digestive tract. A leaky gut can be caused by a variety of factors linked to diet, such as eating
- too much gluten
- a diet overly rich in grains and wheat products
- eating unsprouted nuts and seeds
- and other inflammatory foods which might inflame, pierce, or weaken the lining of the gut over time, such as fast food, convenience foods, junk food, prepackaged foods, foods high in gluten, refined sugar, dairy, and soy.
Many specialists believe that our highly engineered wheat varieties today, such as the kinds used in all popular bread varieties, as well as packaged baked goods, and foods and flours of all kinds are to blame because these hardy types of wheat are engineered to withstand layers of pesticides.
Consequently, they are so porous and splintery, they can literally puncture the tender gut lining not just in one place but many places along that long digestive tract.
A leaky gut, then, leaks toxins and bacteria out into the bloodstream, where it can set off an autoimmune response that causes inflammation and allergies, because of toxins and bad bacteria upon itself, as it begins attacking what it thinks are toxic invaders by assailing these food particles with our immune system (study).
This is one reason why leaky gut causes fatigue. We are using up precious energy to launch the body into defense mode all the time.
This inflammatory response can cause conditions such as migraines, eczema, fatigue, food allergies, arthritis and a range of other conditions (source).
Along with toxins leaking out, however, are toxins which leak in from the bloodstream, which may destroy your fragile bacteria balance in the gut, and, consequently, destroy digestive enzymes that are responsible for nutrient absorption.
This is why leaky gut can cause nutritional deficiencies and must be treated for the long-term health of the body as well as to ease the digestive discomfort it typically causes.
What causes leaky gut?
In most cases of leaky gut, the condition is caused by diet or the quality of foods one eats. For example, gluten is a big cause of leaky gut as noted earlier.
However, we eat a variety of GMO foods today that can irritate or pierce the gut, such as soy, rice, and other kinds of grains used to manufacture bread, muffins, bagels, Pop Tarts, Little Debbies, and other big profit grain food like cereals.
Other inflammatory foods such as soy, dairy, alcohol, and foods that cause fermentation in the gut can also cause swelling and inflammation that lead to leaky gut.
Leaky gut can also be caused or aggravated by medications and OTC drugs such as pain relievers, such as acetaminophen and aspirin, which can irritate the gut lining and damage the mucous layers of the gut.
Of course, antibiotics are very hard in the gut and wipe out whole precious colonies of good bacteria, which can deplete the lining of the gut and make the gut very fragile and easily punctured or inflamed.
See, we desperately need that good bacteria because the lining of our gut is composed of cells that swell, expand, and seal together tightly as they feed on good gut bacteria and foods such as prebiotics, fermented foods, probiotic-rich cultured dairy like yogurt, and vegetable fiber, for example.
So eating a diet rich in foods that can ferment in the gut, like refined grains and sugar, can lead to an imbalance in gut bacteria, that eventually weakens the gut lining, leaving it so fragile it can them be easily punctured by poor-quality grains (source).
What are the symptoms of leaky gut?
The following are the most prominent signs of leaky gut according to gut specialists and gastroenterologists:
- Food allergies
- Seasonal allergies
- A compromised or weak immune system
- Headaches and brain fog
- Chronic diarrhea or constipation, gas, and bloating
- Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s, lupus, or multiple sclerosis.
- Depression and anxiety
- ADHD, bipolar disorder and other mental disorders like these
- Chronic, excessive fatigue
- Memory loss
- Arthritis and joint pain
- Skin rashes, acne, rosacea, eczema
What is the Leaky Gut Diet?
A leaky gut diet is one that focuses on removing all possible foods that can irritate or inflame the gut and then, creating a diet of gut healthy foods that work to nourish and strengthen the gut lining, helping the gut to build up a healthy balance of good and bad bacteria that help us properly digest foods and keep the system optimally healthy.
Gut healing diets focus foods that are fibrous, gut healing, and which nourish that bacteria in the gut, such as fermented foods and yogurts.
In order to heal a leaky gut—you have to fix the problem at its source, which means you have to begin with the diet.

First, focus on elimination
Most individuals find it helpful to focus first on elimination. You cannot heal the gut until you eliminate all foods which might be causing punctures, irritation, or irritation to the gut lining, such as foods you might be allergic to and not even know it.
Most gut specialists and gastroenterologist recommend that individuals eliminate the following foods immediately:
- Gluten (directly tied to leaky gut)
- Grains (contain phytic acid which irritates the gut lining)
- Sugar and sweeteners of all kinds (fermentation of the gut, which leads to yeast overgrowth and a weakened gut lining)
- Industrial seed oils (canola, corn, safflower, cottonseed) Thee oils are very inflammatory and gut inflammation is directly tied to leaky gut
- Foods that prompt an allergic response like nuts, soy, and dairy (until you know if you are allergic to these or that these are definitely not part of the problem, eliminate them for a time)
The FODMAPS and GAPS Diet for Leaky Gut
There are two effective diets that have gained a lot of acclaim for helping to heal leaky gut: the GAPS diet and the FODMAPS diet plan.
The GAPS Diet is a diet that was developed by Dr. Campbell-McBride. It’s a diet that was designed to cure disorders such as Autism and ADHD through a gut healing protocol that eliminates gut-irritating foods and relies on gut healing foods such as steamed vegetables and bone broths.
Dr. Axe has a very comprehensive and easy-to-understand article on how to eat the GAPS way here.
One of the most respected diets for gut healing is a FODMAP- based diet. A FODMAPS diet avoids foods which cause fermentation in the gut, finding healing fermentation provides gut healing overall.
Therefore, proponents of the FODMAPS diet avoid foods in the elimination phase such as:
- high fructose fruits of all kinds
- allium foods such as onions and garlic
- all foods containing lactose
- condiments (they’re high in sugar)
- all refined sugar foods
- and all grains and nuts. For a full list of foods you can and cannot eat on a FODMAPS diet, click
Healing the Gut with The Leaky Gut Diet
In order to repair a leaky gut, besides avoid gut piercing and irritating foods, you also want to add foods which stimulate the gut-healing process and nourish healthy bacteria. The following foods are great ones for doing this.
Bone broths
Making very gelatin-rich bone broths full of marrow-rich bones like chicken feet, veal knuckles, and other bones you can get from a good butcher will help you make broths that literally turn into jello when cooled.
Gelatinous foods help to heal the gut. Gelatin and bone broth contain important amino acids that help seal a leaky gut like proline, glycine, and potassium.
Jello and gelatin
Eat jello or add gelatin, if you can, to hot soups. This is cheaper than packaged bone broths and just as effective. Or, you can learn to make delicious aspics, like bone broth or vegetable aspics made from fibrous vegetables and gelatin.
Kefir, amasai, yogurt, sour cream, buttermilk
Raw, cultured dairy products like the ones listed above will help nourish healthy bacteria in the gut to create a strong new gut lining.
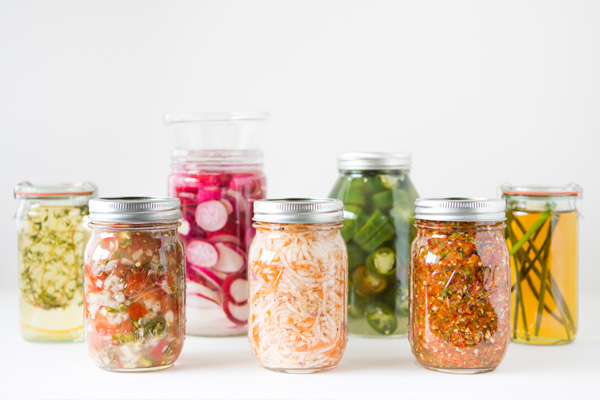

Fermented vegetables
Fermented vegetables like pickles, Kim Chi, beet kvass, and sauerkraut help balance PH in the gut and repair the gut lining.
Fibrous vegetables
High fiber vegetables help restore gut health in all kinds of ways. They give the good bacteria something to “chew and feed” on and this helps the gut cells to swell, go stronger, and seal the gut lining.
Fibrous foods also help flush toxins out of the gut and intestines that have built up from a leaky gut and to balance bacteria in the gut, which further promotes a strong, healthy to gut lining.
High, healthy fats
Egg yolks, fatty fish, and other Omega-3 rich foods help to seal the gut and promote healing. You can also try a fermented cod liver oil supplement, like Blue Ice.
You can fermented cod oil in the refrigerator, it’s consistency is almost like gut-healing jello, by the way, and eat just a ½ tsp. a day to heal the gut.
Supplements that heal the gut
There are all kinds of supplements that can help you achieve a better bacteria of gut bacteria and heal and seal the gut lining.
Digestive enzymes
Digestive enzymes aid the pancreas and gallbladder by helping you produce bile and enzymes needed to absorb nutrients fully again.
With a leaky gut, you have been losing precious nutrients from lack of good bacteria to absorb the nutrients.
Digestive enzymes will assure you’re absorbing nutrients completely again and help you manufacture strong, healthy bile, balance the PH of the gut, and balance bacteria in the gut as well.
DGL licorice
Licorice helps to heal and seal the mucosal lining of the gut. It’s a wonderful supplement for restoring gut health and helping ease stress as well.
L-glutamine powder
L-glutamine is an essential amino acid that helps to heal injured digestive tract linings and can help alleviate chronic diarrhea in leaky gut sufferers as well.
Okra pepsin
Okra pepsin is especially effective at nourishing an impaired gut lining and for helping flush toxins out of the gut as well.
This is important because, with the leaky gut syndrome, you have a lot of toxins in the gut leaking in that shouldn’t be there.
Slippery Elm
Slippery elm, like okra, is high in mucilage, which helps create a new, stronger mucosal lining for the gut and helps to heal inflammation in the stomach lining and gut.
Leaky Gut Shopping List
Fermented foods: Kim Chi, dill pickles, sauerkraut, beet kvass.
Probiotic-rich foods: raw cultured dairy, including yogurt and kefir.
Vegetables for leaky gut: Non-starchy vegetables that are steamed and are easy to digest should form a good bulk of a leaky gut diet.
Try all kinds of vegetables and eat the rainbow, as long as you avoid the starchier varieties (in short, no potatoes, yams, sweet potatoes, turnips, or beets).
Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower are especially good for gut health.
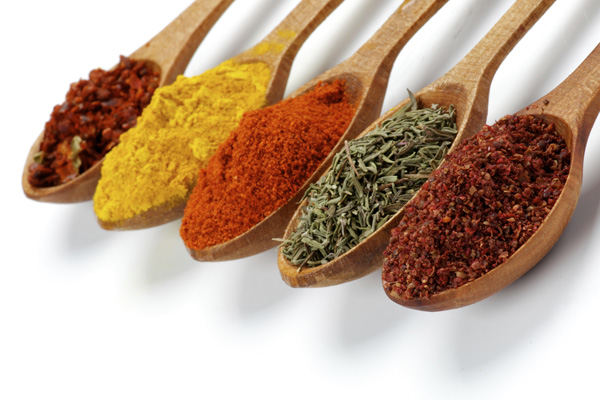

Spices and herbs: turmeric, ginger, licorice tea, peppermint tea, dandelion root tea, and marshmallow root tea are important components of a leaky gut lining, as they are all very gut healing choices.
Bones for broth-making: the best bones for making bone broth are the ones that produce the most gelatinous broths.
Gelatinous broths literally seal the holes in the gut lining, helping you to heal the gut almost immediately. So look for veal knuckles, chicken feet, marrow, and large beef bones.
Overall, the most collagen-rich sources of the animal are best, like knuckles, feet, and marrow. Or you can choose a high-quality bone broth powder.
(You can also simply add packets of gelatin to soups if you’re on a budget—that’s a smart way to make your own gelatinous broths).
Omega 3 rich foods: fatty fish such as sardines, tuna, salmon, and herring, as well as avocados and high-quality grass-fed eggs.
Supplements and herbs: high-quality probiotics, a good krill oil supplement for non-toxic Omega-3s, high-quality cod liver oil, l-glutamine powder, digestive enzymes and/or pancreatic enzymes, slippery elm root, DGL licorice, marshmallow tea, dandelion tea, and okra pepsin are all wonderful for healing and sealing the gut.
How long does it take to heal the gut?
There are over 30 trillion cells in the gut and the length of the gut, when extended, spans some 300 square meters, which is bigger than a large house. So the gut is no tiny organ, and healing it will not take place overnight.
The cells of the gut lining regenerate every two to three weeks, helping you to create a completely new gut lining over time.
But research suggests that to completely heal the gut lining—if you do not have an inflammatory condition, a prescription drug you have to keep taking, or ongoing food sensitivities and allergies—is between two and 12 weeks (study).
Other studies suggest that just three days on a gut healing diet can restore the gut lining (study).
Both studies demonstrate the powerful healing capabilities of the gut when one take measures to avoid gut-irritating foods and to eat gut-healing ones.
How do you know when leaky gut is healed?
When your gut is healed, you are going to notice all kinds of positive changes in your health. Your skin will look healthier because fewer toxins will be entering your system.
Your digestion, of course, will have drastically improved, because you will heal the fermentation in the gut that causes gas, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea.
Another way to know if your gut is improving is to look at your stool. Is it solid and well-formed? The looser your stool is, the more malabsorption is present in the gut, indicating a weak gut lining.
Other ways to tell, for certain, if your gut is healed are to take an Intestinal Permeability test (available online for around $70 to $80 dollars) or to try to add a food back that was irritating your gut before you began your gut-healing protocol, such as dairy or soy, and see if you can digest these more easily now that you have a solid gut lining.
Conclusion
The modern diet and lifestyle are not easy to gut health. In addition to all the toxic foods we have coming in such as vegetables sprayed with pesticides (some of which might not come off with washing), and highly glutinous grains because of hybridization, not to mention the sheer amount of toxins we breathe in every day, which places a great burden on the gut, liver, and kidneys, it is no wonder that the 21st century is seeing such a plethora of gut problems and gut-related diseases.
Many specialists predict we will soon to discover a much wider net of diseases today connected to gut health, as we begin to learn more about how toxins in our environment and toxic foods in our diet may be to blame for many cancers and mental disorders today, such as autism.
It is important, then, to eat a good, organic diet that is rich in plants, to only eat grass-fed meats free of antibiotics and hormones, and to try to avoid gluten, so you can relieve the toxic burden on your gut as much as possible.
Today, we must eat to heal the gut, since most foods we eat today are pretty hard on this fragile organ.
A healthy gut will reward you will health and longevity. Take care of your gut and you can enjoy more energy and a longer life as well.



3 Comments
This was alarming to read, because I can imagine just how poisonous it would be to have leakage in and out of the gut. It would have to be painful over time and sap all the energy out of your body. I was greatly relieved to know that there are foods you can play with to help heal the lining of your gut and return your body to health. I was also happy to hear that there’s a test you can take to find out if the problem has been solved. I’m sure a lot of people will be very glad to have this information, and I appreciate it, too.
All so true..I was so ill with autoimmunity…it turned out its a wheat / gluten allergy..I’ve gotten rid of my sickness through diet
@Andrea you are right that this is alarming to read but the positive side of it is that the situation can be corrected especially that natural food spices can be used for treatment .